Filtrer les publications
Évolution du rivage et des petits-fonds du littoral du Nord de la France depuis le 19ème siècle
La façade nord des Hauts-de-France correspond à une frange côtière de 60 km orientée OSO-ENE ouverte sur la mer du Nord. De nombreux bancs sableux sont présents le long de ce littoral où ils forment des corps sédimentaires massifs parallèles à obliques au trait de côte, localisés sur l’avant-côte jusqu’à plusieurs dizaines de mètres de profondeur. Des levés bathymétriques ont été exécutés depuis les années 1830 dans cette région. Les résultats de ces levés hydrographiques sont conservés au format papier dans les archives du Shom.
A. Latapy, A. Hequette, N. Pouvreau, N. Weber
Date de sortie 05/2018
Date de sortie 05/2018
Paralia - XVème Journées Nationales Génie Côtier – Génie Civil, La Rochelle
Casting light on forcing and breaching scenarios that lead to marine inundation: Combining numerical simulations with a random-forest classification approach
Identifying the offshore forcing and breaching conditions that lead to marine inundation is of high importance for risk management. This task cannot be conducted by using a numerical hydrodynamic model due to its high computation time cost (of several minutes or even hours). In the present study, we show how the random forest (RF) classification technique can approximate the numerical model to explore these critical conditions. We focus on the Bouchôleurs site, which is located on the French Atlantic coast and exposed to overflow processes.
J. Rohmer, D. Idier, F. Paris, R. Pedreros, J. Louisor
Date de sortie 23/03/2018
Date de sortie 23/03/2018
Environmental Modelling & Software, volume 104

Scalable Interactive Platform for Geographic Evaluation of Sea-Level Rise Impact Combining High-Performance Computing and WebGIS Client
As the climate is changing, more applied information on resulting impacts are required to inform adaptation planning . Over the last decade, the amount of information relevant to climate change impact assessment has grown drastically. This can particularly be illustrated in coastal areas, threatened by sea-level rise due to climate change, where a key recent development has been the delivery of precise and accurate topography obtained by Light Detection and Ranging (Li-DAR) at regional and national scales, i.e., respectively, large and small scales.
A. Tellez-Arenas, R. Quique, F. Boulahya, G. Le Cozannet, F. Paris, S. Le Roy, F. Dupros, F. Robida
Date de sortie 21/03/2018
Date de sortie 21/03/2018
Communicating Climate Change Information for Decision-Making

Tidal downscaling from the open ocean to the coast: a new approach applied to the Bay of Biscay
Downscaling physical processes from a large scale to a regional scale 3D model is a recurrent issue in coastal processes studies. The choice of boundary conditions will often greatly influence the solution within the 3D circulation model. In some regions, tides play a key role in coastal dynamics and must be accurately represented. The Bay of Biscay is one of these regions, with highly energetic tides influencing coastal circulation and river plume dynamics.
F. Toublanc, N.K. Ayouba, F. Lyarda, P. Marsaleixb, D.J. Allaina
Date de sortie 20/02/2018
Date de sortie 20/02/2018
Ocean Modelling, volume 124
Monitoring Sea Level and Topography of Coastal Lagoons Using Satellite Radar Altimetry: The Example of the Arcachon Bay in the Bay of Biscay
Radar altimetry was initially designed to measure the marine geoid. Thanks to the improvement in the orbit determination from the meter to the centimeter level, this technique has been providing accurate measurements of the sea surface topography over the open ocean since the launch of Topex/Poseidon in 1992. In spite of a decrease in the performance over land and coastal areas, it is now commonly used over these surfaces. This study presents a semi-automatic method that allows us to discriminate between acquisitions performed at high tides and low tides.
E. Salameh, F. Frappart, V. Marieu, A. Spodar, J.-P. Parisot, V. Hanquiez, I.Turki, B. Laignel
Date de sortie 14/02/2018
Date de sortie 14/02/2018
Remote Sensing, volume 10
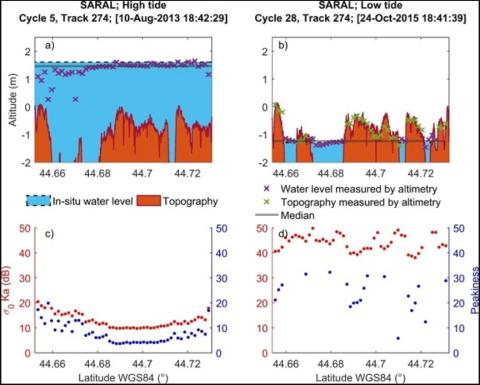
Multi-Satellite Altimeter Validation along the French Atlantic Coast in the Southern Bay of Biscay from ERS-2 to SARAL
Monitoring changes in coastal sea levels is necessary given the impacts of climate change. Information on the sea level and its changes are important parameters in connection to climate change processes. In this study, radar altimetry data from successive satellite missions, European Remote Sensing-2 (ERS-2), Jason-1, Envisat, Jason-2, and Satellite with ARgos and ALtiKa (SARAL), were used to measure sea surface heights (SSH). Altimetry-derived SSH was validated for the southern Bay of Biscay, using records from seven tide gauges located along the French Atlantic coast.
P. L. Vu, F. Frappart, J. Darrozes, V. Marieu, F. Blarel, G. Ramillien, P. Bonnefond, F. Birol
Date de sortie 11/01/2018
Date de sortie 11/01/2018
Remote Sensing, volume 10
![Timeline for radar altimeters used in our study (modified from [25]).](/sites/default/files/styles/large/public/2025-01/radar.png?itok=st25gSb3)
Azimuth selection for sea level measurements using geodetic GPS receivers
Based on analysis of Global Positioning System (GPS) multipath signals recorded by a geodetic GPS receiver, GPS Reflectometry (GPS-R) has demonstrated unique advantages in relation to sea level monitoring. Founded on multipath reflectometry theory, sea level changes can be measured by GPS-R through spectral analysis of recorded signal-to-noise ratio data. However, prior to estimating multipath parameters, it is necessary to define azimuth and elevation angle mask to ensure the reflecting zones are on water.
X. Wang, Q. Zhang, S. Zhang
Date de sortie 10/01/2018
Date de sortie 10/01/2018
Advances in Space Research, volume 61

Coastal monitoring solutions of the geomorphological response of beach-dune systems using multi-temporal LiDAR datasets (Vendée coast, France)
Shield volcanoes are described as low-angle edifices built primarily by the accumulation of successive lava flows. This generic view of shield volcano morphology is based on a limited number of monogenetic shields from Iceland and Mexico, and a small set of large oceanic islands (Hawaii, Galápagos). Here, the morphometry of 158 monogenetic and polygenetic shield volcanoes is analyzed quantitatively from 90-meter resolution SRTM DEMs using the MORVOLC algorithm.
B. Le Mauff, M. Juigner, M. Robin, P. Launeau, P. Fattal
Date de sortie 05/01/2018
Date de sortie 05/01/2018
Geomorphology, volume 304

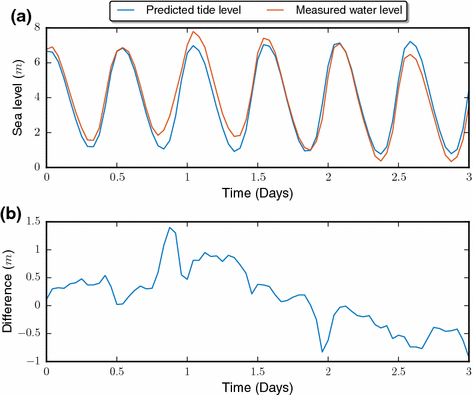
Nonlinear dynamics of the sea level time series in the eastern English Channel
Coastal flooding due to surge events represents natural hazards with huge potential consequences for coastal regions. Sea level time series display variations on a large range of timescales, with a deterministic component associated with tidal variations and a stochastic component primarily associated with meteorological forcing, the non-tidal residual. The deterministic component can be evaluated using a model taking into account astronomical forcing and topographic information.
F. G. Schmitt, A. Crapoulet, A. Hequette, Y. Huang
Natural Hazards, volume 91