
Filtrer les publications
The contribution of short-waves in storm surges: Two case studies in the Bay of Biscay
This study investigates the contributions of short waves in storm surges through the hindcast of two storms that hit the central part of the Bay of Biscay recently. Despite displaying comparable wind speed and directions in the study area, these two storms induced different storm surges and sea states. Xynthia (27–28th of February 2010) was characterized by large (up to 7 m significant wave height Hs) and short-period waves and induced an exceptional storm surge, locally larger than 1.6 m.
X. Bertin , K. Li, A. Roland, J.-R. Bidlot
Continental Shelf Research, volume 96

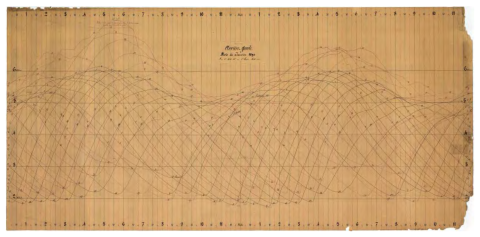
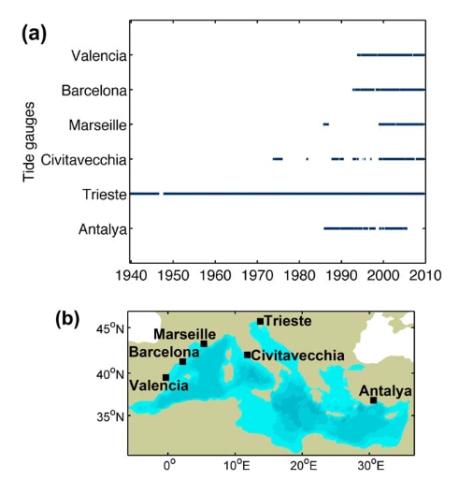
Rapport technique final du projet NIVEXT - NIVeaux EXTrêmes
Ce rapport rend compte du travail effectué dans le cadre du projet NIVEXT financé par la DGPR. Le SHOM disposant de mesures marégraphiques sur les côtes françaises depuis 1850, en base de données numériques ou en dormance sous forme papier dans les archives, la possibilité d’établir un bilan de ce que ces données peuvent apporter à la connaissance des niveaux extrêmes est apparue une action nécessaire et cohérente avec la ligne portée par l’Etat.
C. Daubord
Date de sortie 2015
Date de sortie 2015
Shom
Fortnightly tidal asymmetry inversions and perspectives on sediment dynamics in a macrotidal estuary (Charente, France)
Tidal asymmetry is a phenomenon that characterises estuarine hydrodynamics and has a strong impact on sediment dynamics. Extensive research has been dedicated to studying tidal dynamics in semidiurnal macrotidal estuaries, highlighting several general principles. The ratio of flood to ebb peak velocities and differences in ebb and flood durations are often used to characterise the asymmetry encountered in estuaries.
F. Toublanc, I. Brenon, T. Coulombier, O. Le Moine
Date de sortie 31/12/2014
Date de sortie 31/12/2014
Continental Shelf Research, volume 94

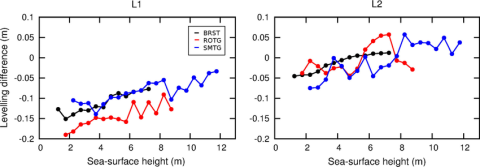
Levelling co-located GNSS and tide gauge stations using GNSS reflectometry
The GNSS reflectometry technique provides geometric information on the environment surrounding the GNSS antenna including the vertical distance to a reflecting surface. We use sea-surface reflections of GPS signals, recorded as oscillations in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), to estimate the GNSS to tide gauge (TG) levelling tie, and thus the ellipsoidal heights of the TG. We develop approaches to isolate SNR data dominated by sea-surface reflections and to remove SNR frequency changes caused by the dynamic sea surface.
A. Santamaría-Gómez, C. Watson, M. Gravelle, M. King, G. Wöppelmann
Date de sortie 20/12/2014
Date de sortie 20/12/2014
Journal of Geodesy, volume 89
Improving the estimation of extreme sea levels by a characterization of the dependence of skew surges on high tidal levels
The knowledge of the statistical distribution of extreme sea levels at the coast is of utmost importance for the characterization of flood risks in coastal areas. In this study we consider that the sea level results from two components: the (astronomical) tide and the (meteorological) surge, without considering the effects of waves. We focus our attention on the dependence of the surge height on the tidal level. At sites with a strong tidal range, the classical analysis methods rely on working only with high tide data (namely high tidal levels and skew surges).
X. Kergadallan, P. Bernardara, M. Benoit, C. Daubord
Date de sortie 02/12/2014
Date de sortie 02/12/2014
Proceedings of 34th Conference on Coastal Engineering, Seoul, Korea
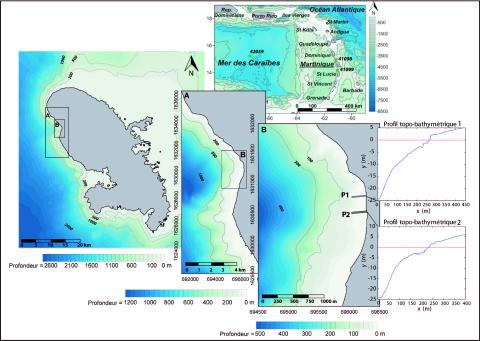
Modélisation des niveaux marins extrêmes associés à la circulation des cyclones Lenny (1999) et Omar (2008), commune de saint-pierre, littoral nord-ouest de la Martinique
Les submersions marines sont le plus souvent associées à des conditions météorologiques locales de tempête et aux phénomènes bien connus de surcote résultant du cumul de l’effet barométrique inverse et des vents d'afflux. Le déferlement des vagues joue également un rôle prépondérant dans la surélévation totale. Il provoque des variations du niveau d’eau de deux types : une surélévation statique du niveau moyen (surcote de vague) et des variations instantanées provoquées par le jet de rive. Ces deux phénomènes sont responsables dans certains cas de plus de 2/3 de la surélévation totale.
A. N. Lerma, Y.-F. Thomas, P. Saffache, P. Durand, M. Lamy
Date de sortie 12/2014
Date de sortie 12/2014
Vertigo, volume 14
The ability of a barotropic model to simulate sea level extremes of meteorological origin in the Mediterranean Sea, including those caused by explosive cyclones
Storm surges are responsible for great damage to coastal property and loss of life every year. Coastal management and adaptation practices are essential to reduce such damage. Numerical models provide a useful tool for informing these practices as they simulate sea level with high spatial resolution. Here we investigate the ability of a barotropic version of the HAMSOM model to simulate sea level extremes of meteorological origin in the Mediterranean Sea, including those caused by explosive cyclones.
F. M. Calafat, E. Avgoustoglou, G. Jordà, H. Flocas, G. Zodiatis, M. N. Tsimplis, J. Kouroutzoglou
Date de sortie 31/10/2014
Date de sortie 31/10/2014
JGR Oceans, volume 119
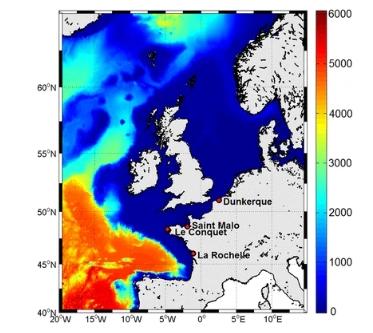
Atmospheric storm surge modeling methodology along the French (Atlantic and English Channel) coast
Storm surge modeling and forecast are the key issues for coastal risk early warning systems. As a general objective, this study aims at improving high-frequency storm surge variations modeling within the PREVIMER system (www.previmer.org), along the French Atlantic and English Channel coasts. The paper focuses on (1) sea surface drag parameterization and (2) uncertainties induced by the meteorological data quality. The modeling is based on the shallow-water version of the model for applications at regional scale (MARS), with a 2-km spatial resolution.
H. Muller, L. Pineau-Guillou, D. Idier, F. Ardhuin
Date de sortie 16/10/2014
Date de sortie 16/10/2014
Ocean Dynamics, volume 64
Storm impact on the seasonal shoreline dynamics of a meso- to macrotidal open sandy beach (Biscarrosse, France)
A three-year dataset (2007–2010) of shoreline and sandbar positions derived from video observations of an open sandy beach (Biscarrosse, France) is analyzed, to explore the impact of storms on the seasonal shoreline dynamics. The results indicate that a clear seasonality is observed in the offshore significant wave height and in the occurrence of ‘winter storm’ events that are defined as periods with significant wave height greater than 4 m lasting at least 12 h.
N. Senechal, G. Coco, B. Castelle, V. Marieu
Date de sortie 13/10/2014
Date de sortie 13/10/2014
Geomorphology, volume 228
