
Filtrer les publications
Rôle des observations pour estimer et comprendre la hausse du niveau de la mer
Le niveau de la mer s’élève aujourd’hui à un rythme accéléré, c’est ce que montrent les satellites altimétriques qui le surveillent en routine depuis plus de trois décennies. Grâce à différents systèmes d’observations indépendants, les causes de l’élévation du niveau moyen global des mers sont désormais bien quantifiées. Les deux contributions principales sont le réchauffement de l’océan, qui se dilate, et la fonte des glaces continentales, deux phénomènes induits par le changement climatique.
Anny Cazenave, Lancelot Leclercq
Date de sortie 02/2026
Date de sortie 02/2026
La Météorologie, n°132
On the use of SWOT altimetry data for monitoring coastal hydrodynamics
Satellite altimetry has proven highly effective for monitoring sea surface variability in open oceans and continental shelves, yet its extension to nearshore environments remains challenging. Within the framework of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) wide-swath interferometric mission, this study evaluates SWOT’s capability to retrieve coastal Sea Surface Heights (SSH) and Significant Wave Heights (SWH) in the English Channel along the UK and French coasts.
E.I. Turki, M.S. Islam, C. Lopez Solano, E. Salameh, M. Domingues, T. Mendoza, L. Aouf, L. Froideval, D. Gutierrez Barcelo, B. Laignel, A. Carbonniere, F. Frappart
Date de sortie 29/11/2025
Date de sortie 29/11/2025
International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation
GNSS-IR real-time water level retrieval method based on hybrid sliding window and LSTM
Real-time water level monitoring is of critical significance in flood disaster mitigation and water resource management. This paper proposes a real-time Global Navigation Satellite System Interferometric Reflectometry (GNSS-IR) water level retrieval method based on the hybrid integration of sliding window and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM). By dynamically updating input sequences through the sliding window mechanism, an LSTM model captures both temporal and nonlinear characteristics of water level variations, enabling high-precision real-time prediction.
Peiyuan Wang, Fang Cheng, Junqiang Han, Zhen Jiang, Yang Liu, Rui Tu, Xiaolei Wang, Weisheng Wang, Bayin Dalai, Gulayozov Majid Shonazarovich, Yaoming Li, Xiaochun Lu
Date de sortie 28/10/2025
Date de sortie 28/10/2025
Science of Remote Sensing, Volume 12

Towards 0.1mm/yr stability over decades for measuring sea level using tide gauges together with GNSS-based instruments?
Precise and stable measurements of sea level are critical for understanding long-term climate trends. This study investigates the stability of sea level measurements using tide gauges and GNSS-based instruments at the Corsica calibration site. The calibration and validation of satellite altimetry missions require an uncertainty of ± 0.3 mm/yr at a global scale and ± 1 mm/yr at a regional scale. The study also evaluates the vertical land motion (VLM) of the reference GNSS site (RG00) and its impact on long-term sea level trends.
Pascal Bonnefond, Olivier Laurain, Pierre Exertier, Michel Calzas, Christine Drezen, Lionel Fichen, Antoine Guillot, Thierry Guinle, Nicolas Picot
Date de sortie 17/08/2025
Date de sortie 17/08/2025
Marine Geodesy
Spatial and Temporal Variability in Tide‐Induced Icequake Activity at the Astrolabe Coastal Glacier, East Antarctica
The grounding zones (GZ) of marine‐terminating glaciers, where ice transitions from grounded to floating, experience strong mechanical changes in response to ocean tides. The spatial and temporal dynamics of these changes remain poorly documented, as they require multi‐scale observations capable of resolving internal ice deformation. Here, we use seismic observations, collected across different years and various scales, coupled with GNSS observations, to evaluate the brittle deformation at the GZ and shear margins of the Astrolabe Glacier (East Antarctica, Terre Adélie).
Tifenn Le Bris, Guilhem Barruol, Florent Gimbert, Emmanuel Le Meur, Dimitri Zigone, Anuar Togaibekov, Denis Lombardi, Maxime Bès de Berc, Armelle Bernard
Date de sortie 13/08/2025
Date de sortie 13/08/2025
Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 130, e2024JF008054.
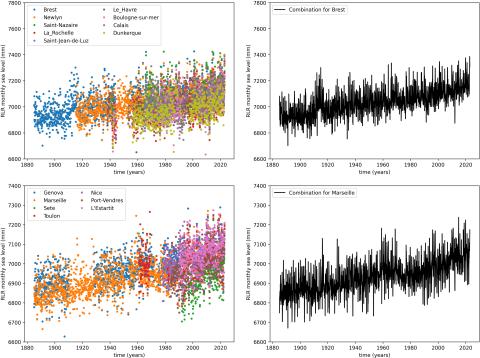
Observational uncertainties on past and future sea level rise for Marseille and Brest tide gauges
Brest and Marseille tide gauges time series between 1885 and 2022 data gaps are filled with data from neighboring tide gauges thanks to a combination model that does not alter original trends. Continuous relative sea level time series obtained from this step are then corrected from the inverse barometer effect and/or periodic components. Time series are systematically explored to form all possible sub-time series, from 20 years length to the full time span, and adjusted with linear and quadratic fits.
Jonathan Chenal
Date de sortie 30/07/2025
Date de sortie 30/07/2025
Comptes Rendus. Géoscience, Volume 357 (2025), pp. 349-368
An SWE-FEM Model with Application to Resonant Periods and Tide Components in the Western Mediterranean Sea Region
A FEM model of Shallow Wave Equations (SWE-FEM) is studied, taking into account the variable bathymetry of semi-enclosed sea basins. The model, with a spatially varying Coriolis term, is implemented for the description of combined refraction–diffraction effects, from which the eigenperiods and eigenmodes of extended geographical sea areas are calculated by means of a low-order FEM scheme. The model is applied to the western Mediterranean basin, illustrating its versatility to easily include the effects of geographical characteristics like islands and other coastal features.
Kostas Belibassakis, Vincent Rey
Date de sortie 30/06/2025
Date de sortie 30/06/2025
Journal of Marine Science and Engineering
Reconstruction de la série marégraphique historique d’Antsiranana (Diego-Suarez) à Madagascar
Ce stage s’inscrit dans le cadre des activités de valorisation des archives marégraphiques, visant à reconstituer et diffuser une série chronologique du niveau de la mer pour Antsiranana (Madagascar). Le port d’Antsiranana, extrémité nord de Madagascar, dispose d’un marégraphe permanent depuis 1902, avec des observations nominales de 1888 à 1970. Ce site stratégique est l’une des rares archives longues de l’océan Indien occidental, une zone encore peu documentée (Wenzel et al., 2014).
Léo SCHAFFER
Date de sortie 27/06/2025
Date de sortie 27/06/2025
Master 2, Sciences de la Terre, Planètes, Environnement, Université de Bretagne Sud (UBS)
Evaluation and combination of quad-constellation multi-GNSS multipath reflectometry applied to sea level retrieval
The satellites of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) continuously broadcast L-band signals at about a 20-cm wavelength. Some signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) data received by off-shelf geodetic antennas contain the multipath information of the sea, and they have been demonstrated for use in retrieving sea levels; however, compared with conventional tide gauges, this GNSS multipath reflectometry (GNSS-MR) technique is limited in terms of both precision and sampling rate.
X. Wang, X. He, Q. Zhang
Date de sortie 19/06/2025
Date de sortie 19/06/2025
Remote Sensing of Environment, volume 231
