
Filtrer les publications
The contribution of short-wave breaking to storm surges: The case Klaus in the Southern Bay of Biscay
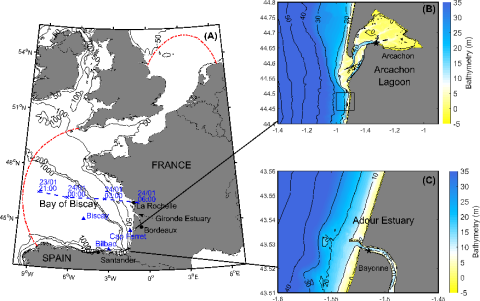
This study investigates the contribution of short-wave breaking to storm surges through a high-resolution hindcast of the sea state and storm surge associated with the extra-tropical storm Klaus. This storm made landfall in January 2009 in the Southern Bay of Biscay and produced the largest storm surges observed in this region over the last 20 years, with 1.70 m in the Arcachon Lagoon and 1.10 m in the Adour Estuary.
L. Lavaud, X. Bertin, K. Martins, G. Arnaud, M.-N. Bouin
Date de sortie 17/10/2020
Date de sortie 17/10/2020
Ocean Modelling, volume 156
Assessment of the Shoreline Evolution at the Eastern Giens Tombolo of France
Giens double tombolo linking Giens island to the mainland is a unique geomorphological formation in the world. However, its existence has been threatened by coastal erosion, especially in the eastern part of this tombolo. The investigation of historical shoreline changes along the eastern Giens tombolo were carried out applying the integration of satellite remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS) techniques. Additionally, the combination of the Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) and linear regression method was used to predict the location of future shorelines.
M. T. Vu, Y. Lacroix, Q. H. Vu
Date de sortie 09/10/2020
Date de sortie 09/10/2020
Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovations for Sustainable and Responsible Mining, Springer, Cham

Influence des modifications morphologiques de l'avant-côte sur l'hydrodynamisme et l'évolution du littoral des Hauts-de-France depuis le XIXe siècle
Dans les environnements côtiers, les interactions entre les processus morphodynamiques, océanographiques et anthropiques (agissant sur différentes échelles de temps) contrôlent l'évolution des systèmes littoraux. Cette thèse est axée sur une échelle de temps séculaire afin de déterminer l'influence non seulement des activités humaines, mais aussi l'impact du changement climatique.
A. Latapy
Date de sortie 15/07/2020
Date de sortie 15/07/2020
Université Littoral Côte d'Opale - LOG

The Seasonal Cycle of Mean Sea Level in the North East Atlantic Ocean
The analysis of long-term tide gauge data collected in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean reveals that the seasonal cycle of mean sea level (hereafter MSL) exhibits amplitudes of up to 0.4 m. The position of MSL is of fundamental importance for many issues such as storm-induced flooding or the morphodynamics of shallow inlets, yet the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. We characterize the seasonal cycle based on field observations complemented with a numerical hindcast.
M. Payo-Payo, X. Bertin
Date de sortie 26/05/2020
Date de sortie 26/05/2020
Journal of Coastal Research, volume 95

Assessing the Role of Storm Waves and River Discharge on Sediment Bypassing Mechanisms at the Têt River Mouth in the Mediterranean (Southeast France)
River mouths along sandy coastlines are influenced by alongshore transport of littoral sands and the interaction of hydrodynamics processes at the river mouth. These interaction are responsible for opening/closure of river outlets and subsequent episodes of sand bypassing by spitbreaching. Here, we study these mechanisms of alongshore sediment bypassing at a river mouth along the French Mediterranean coast. Over the last 6 years, bypassing processes were found to be associated with spit elongation and spit breaching.
Y. Balouin, F. Bourrin, F. Meslard, E. Palvadeau, N. Robin
Date de sortie 26/05/2020
Date de sortie 26/05/2020
Journal of Coastal research, volume 95

Intertidal topography mapping using the waterline method from Sentinel-1 & -2 images: The examples of Arcachon and Veys Bays in France
Intertidal flats lying as a buffer zone between land and sea provide critical services including protection against storm surges and coastal flooding. These environments are characterized by a continuous redistribution of sediment and changes in topography. Sea level rise, anthropogenic pressures, and their related stressors have a considerable impact on these areas and are expected to put them under more stress; hence the increased need for frequent and updated topography maps.
E. Salameh, F. Frappart, I. Turki, B. Laignel
Date de sortie 13/05/2020
Date de sortie 13/05/2020
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, volume 163

Quality control of in situ sea level observations: a review and progress towards automated quality control - Volume 1
The Global Sea-Level Observing System (GLOSS, https://www.gloss-sealevel.org/) is an international programme conducted under the auspices of the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC)of UNESCO. GLOSS aims at the establishment of high quality global and regional sea level networks for application to climate, oceanographic and coastal sea level research. The programme became known as GLOSS as it provides data for deriving the 'Global Level of the Sea Surface'.
Commission océanographique intergouvernementale
Date de sortie 05/2020
Date de sortie 05/2020
UNESCO

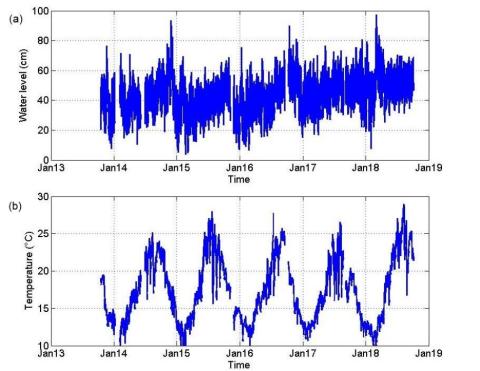
On the use of long term observation of water level and temperature along the shore for a better understanding of the dynamics: Example of Toulon area, France
A dense network of instruments has been deployed within harbors along the Mediterranean coast, in the Toulon Metropole area, between the Hyères islands and the Sanary Bay in the framework of the observation network HTM-NET. Each station is equipped with two piezometric sensors, the first immersed and the second emerged, which allows the calculation of the water level. Both piezometric sensors are also equipped with a temperature sensor. Water level and temperature data are analyzed and discussed, also considering meteorological data provided by Météo-France stations.
V. Rey, C. Dufresne, J.-L. Fuda, D. Mallarino, T. Missamou, C. Paugam, G. Rougier, I. Taupier-Letage
Date de sortie 24/03/2020
Date de sortie 24/03/2020
Ocean Dynamics, volume 70
Coherent superposition of multi-GNSS wavelet analysis periodogram for sea-level retrieval in GNSS multipath reflectometry
The multipath signals of GNSS can act as a tide gauge via a technology called Global Navigation Satellite Systems multipath reflectometry (GNSS-MR), which is based on the relationship between multipath frequency and height to sea surface. In addition to the traditional frequency extraction method of Lomb–Scargle periodogram (LSP), wavelet analysis can be applied to extract instantaneous multipath frequencies of GPS L1, thus improving data utilization.
X. Wang, X. He, Q. Zhang
Date de sortie 31/12/2019
Date de sortie 31/12/2019
Advances in Space Research, volume 65
