Filtrer les publications
Coherent superposition of multi-GNSS wavelet analysis periodogram for sea-level retrieval in GNSS multipath reflectometry
The multipath signals of GNSS can act as a tide gauge via a technology called Global Navigation Satellite Systems multipath reflectometry (GNSS-MR), which is based on the relationship between multipath frequency and height to sea surface. In addition to the traditional frequency extraction method of Lomb–Scargle periodogram (LSP), wavelet analysis can be applied to extract instantaneous multipath frequencies of GPS L1, thus improving data utilization.
X. Wang, X. He, Q. Zhang
Date de sortie 31/12/2019
Date de sortie 31/12/2019
Advances in Space Research, volume 65

Decadal-scale Dynamics and Morphological Evolution of Mangroves and Beaches in a Reef-lagoon Complex, Mayotte Island
Mayotte Island is characterized by a vast coral reef-lagoon complex comprising significant mangrove development and numerous pocket beaches nested between volcanic headlands. Since 2005, field experiments involving topographic surveys, observations and hydrodynamic measurements have been coupled with the analysis of aerial photographs (1950-2016) in order to improve understanding of the morphodynamic interactions between mangroves, beaches and the coral reefs.
M. Jeanson, F. Dolique, E. J. Anthony, A. Aubry
Date de sortie 11/12/2019
Date de sortie 11/12/2019
Journal of Coastal Research, volume 88

Characterization of Sea-level Variations Along the Metropolitan Coasts of France: Waves, Tides, Storm Surges and Long-term Changes
With 5853 km of coastlines facing the North Sea, the English Channel, the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea, France displays littoral zones exposed to a wide spectrum of wave climates, tidal ranges and storm surges. This study aims at characterizing in a systematic way sea level variations along the coasts of France. Wave climates are first characterized using state-of-the-art high resolution hindcasts validated against available observations from the national network CANDHIS.
G. Dodet, X. Bertin, F. Bouchette, M. Gravelle, L. Testut, G. Wöppelmann
Date de sortie 11/12/2019
Date de sortie 11/12/2019
Journal of Coastal Research, volume 88

Modélisation déterministe et probabiliste des dommages assurantiels causés par les phénomènes de submersion marine en France métropolitaine
Afin d'anticiper les dommages engendrés par les phénomènes de submersion marine et d'y faire face, CCR a développé un modèle spécifique à ce péril pour la France métropolitaine. Ce modèle présente deux volets : une modélisation déterministe permettant d'estimer le coût d'un événement quelques jours après sa survenance et une modélisation probabiliste permettant d'estimer l'exposition au risque de submersion marine.
J.-P. Naulin, D. Moncoulon, A. Quantin
Date de sortie 13/11/2019
Date de sortie 13/11/2019
La Houille Blanche
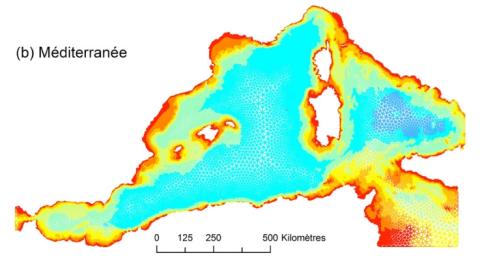
2D and 3D modelling of offshore sandbank dynamics
The coastal zone is an important resource both socially and economically. Globally, coastal zones are under increasing threat from the effects of climate change, erosion and flooding. Understanding the mechanisms of coastal processes is key to the long term management and protection of the coastal zone and its resources. Sandbanks are large sedimentary bodies found on coastal shelves worldwide that protect nearby coastlines from the effects of erosion. This research aims to model the hydrodynamics and morphodynamics of the sandbanks in the southern bight of the North Sea, UK.
S. Clee, S. Pan
Date de sortie 09/2019
Date de sortie 09/2019
E-proceedings of the 38th IAHR World Congress, Panama City, Panama
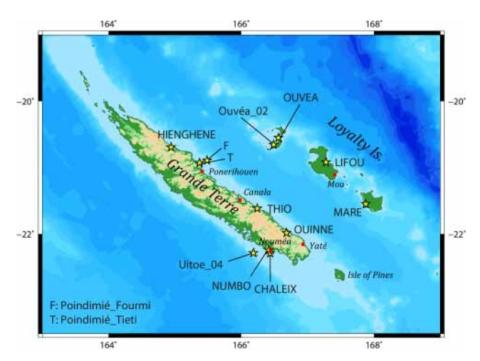
Update of the tsunami catalogue of New Caledonia using a decision table based on seimic data and maregraphic records
Fourteen years ago, the 26 December 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami demonstrated the destructional capability of tsunamis to the entire world. Since then, many research programs have been initiated to try to understand the phenomenon and its related hazards better and to improve the early warning systems for exposed coastal populations. Pacific Islands Countries and Territories (PICTs) are especially vulnerable to tsunamis. Amongst them, New Caledonia is a French overseas territory located in the Southwest Pacific and exposed to several tsunami sources.
J. Roger, B. Pelletier, J. Aucan
Date de sortie 22/07/2019
Date de sortie 22/07/2019
NHESS
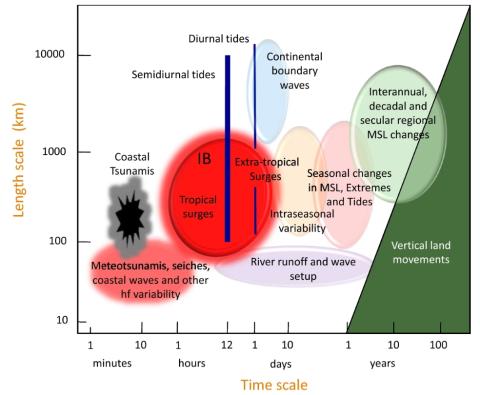
Forcing Factors Affecting Sea Level Changes at the Coast
We review the characteristics of sea level variability at the coast focussing on how it differs from the variability in the nearby deep ocean. Sea level variability occurs on all timescales, with processes at higher frequencies tending to have a larger magnitude at the coast due to resonance and other dynamics. In the case of some processes, such as the tides, the presence of the coast and the shallow waters of the shelves results in the processes being considerably more complex than offshore.
P. L. Woodworth, A. Melet, M. Marcos, R. D. Ray, G. Wöppelmann, Y. N. Sasaki, M. Cirano, A. Hibbert, J. M. Huthnance, S. Monserrat, M. A. Merrifield
Date de sortie 08/05/2019
Date de sortie 08/05/2019
Surveys in Geophysics, volume 40
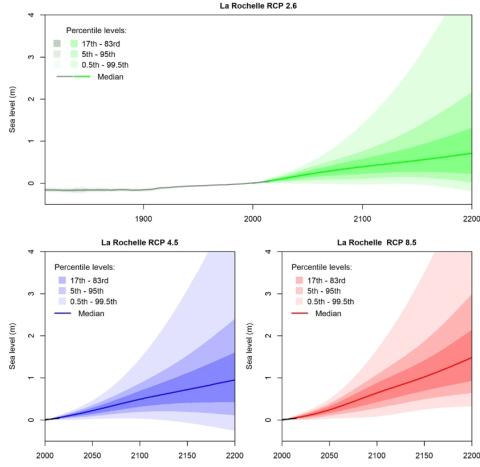
Quantifying uncertainties of sandy shoreline change projections as sea level rises
Sandy shorelines are constantly evolving, threatening frequently human assets such as buildings or transport infrastructure. In these environments, sea-level rise will exacerbate coastal erosion to an amount which remains uncertain. Sandy shoreline change projections inherit the uncertainties of future mean sea-level changes, of vertical ground motions, and of other natural and anthropogenic processes affecting shoreline change variability and trends. Furthermore, the erosive impact of sea-level rise itself can be quantified using two fundamentally different models.
G. Le Cozannet, T. Bulteau, B. Castelle, R. Ranasinghe, G. Wöppelmann, J. Rohmer, N. Bernon, D. Idier, J. Louisor, D. Salas-y-Mélia
Date de sortie 11/04/2019
Date de sortie 11/04/2019
Scientific Reports, volume 9, article 42
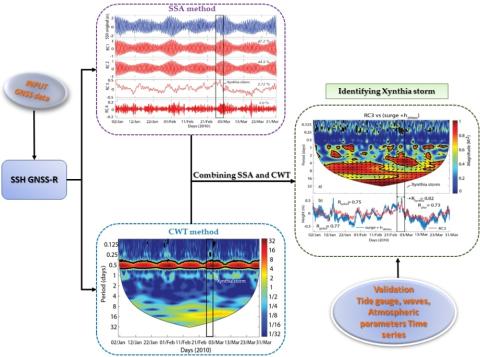
Identifying 2010 Xynthia Storm Signature in GNSS-R-Based Tide Records
In this study, three months of records (January–March 2010) that were acquired by a geodetic Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) station from the permanent network of RGP (Réseau GNSS Permanent), which was deployed by the French Geographic Institute (IGNF), located in Socoa, in the south of the Bay of Biscay, were used to determine the tide components and identify the signature of storms on the signal to noise ratio (SNR) during winter 2010.
P. Lan Vu, M. Cuong Ha, F. Frappart, J. Darrozes, G. Ramillien, G. Dufrechou, P. Gegout, D. Morichon, P. Bonneton
Date de sortie 01/04/2019
Date de sortie 01/04/2019
Remote Sensing, volume 11